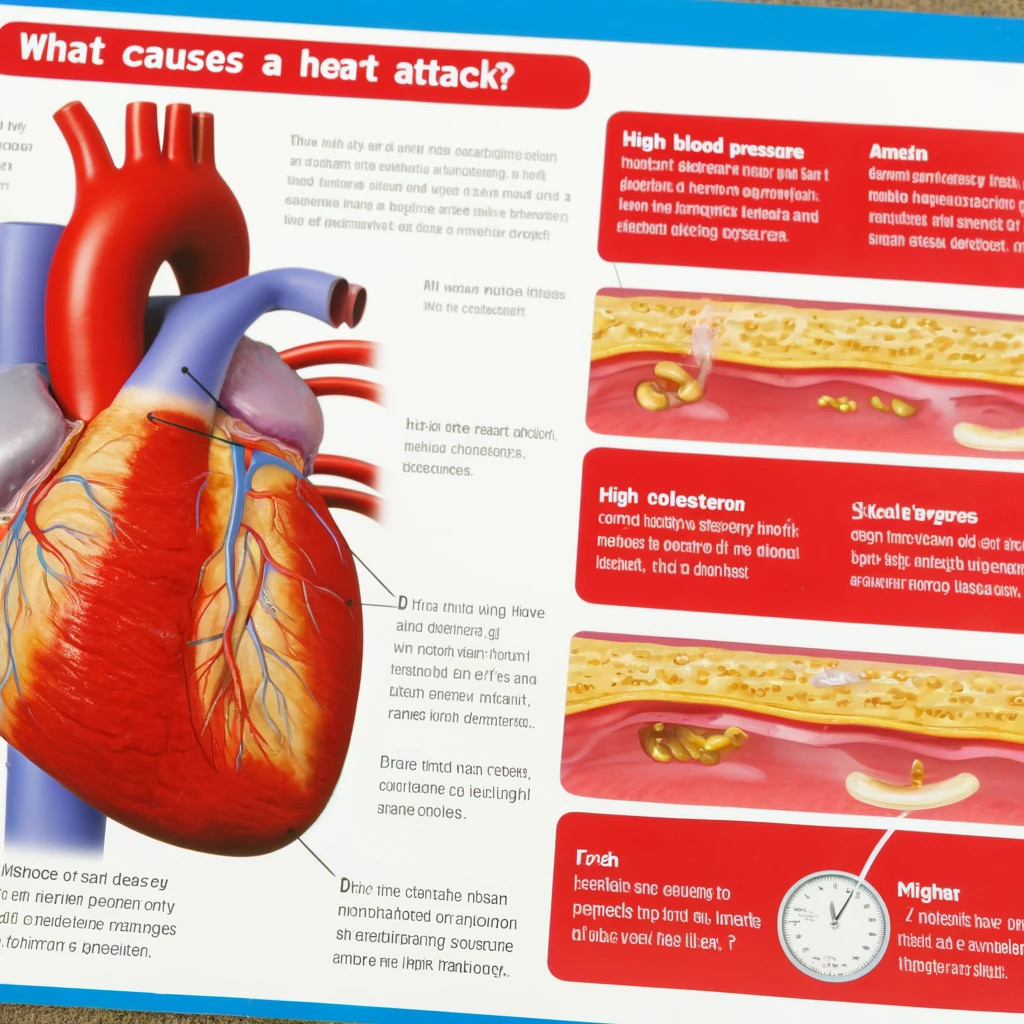
What Causes a Heart Attack? Unraveling the Triggers and Mechanisms Behind Cardiac Events
Understanding what causes a heart attack is crucial for both prevention and management of one of the leading causes of death worldwide. A heart attack, medically known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of the heart suddenly becomes blocked, and the heart can’t get oxygen. If blood flow isn’t restored quickly, the section of heart muscle begins to die. This comprehensive article explores the various factors and conditions that lead to a heart attack, offering insights into how these can be managed or mitigate

The Role of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
The primary cause of a heart attack is coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart with blood, oxygen, and nutrients (coronary arteries) become damaged or diseased. Cholesterol-containing deposits (plaque) in your arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease.
Plaque Buildup and Rupture
Over time, plaque can build up along the course of an artery and harden, which narrows the arteries and reduces the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Sometimes, the plaque can rupture (break open) and form a clot that blocks the flow of blood. The interruption in blood flow can damage or destroy part of the heart muscle, leading to a heart attack.
Risk Factors Contributing to Heart Attacks
Several risk factors play a significant role in the development of plaque buildup and arterial damage:
- High blood pressure: Over time, high blood pressure can damage arteries that feed your heart by accelerating arteriosclerosis, the hardening of the arteries.
- High cholesterol levels: High levels of cholesterol in your blood can increase the risk of formation of plaque and atherosclerosis.
- Smoking: Chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases your risk of a heart attack by speeding up atherosclerosis and increasing cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Obesity is linked with high blood cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise is associated with many forms of heart disease, including heart attacks.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices also have a significant impact on the risk of having a heart attack:
- Diet: Eating a diet that’s high in fat, salt, sugar, and cholesterol can contribute directly to the development of heart disease.
- Alcohol use: Excessive alcohol use can lead to heart muscle damage.
- Stress: Stress may damage arteries and worsen other risk factors for heart disease.
- Drug abuse: Using stimulants like cocaine or amphetamines can trigger a spasm of your coronary arteries that can cause a heart attack.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can also play a role in an individual’s likelihood of developing heart disease. Family history of heart disease increases the risk of coronary artery disease, especially if a parent developed it at an early age.
Age and Gender
Age and gender are important risk factors too. Men are generally at greater risk of a heart attack. The risk for women increases and can be similar to that of men after reaching menopause.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including exposure to air pollution, have been linked to higher heart attack risks due to their influence on heart rate variability and inflammation in the body.
Prevention and Management
Preventing heart attacks involves managing risk factors through lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Steps include maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and not smoking. For those with heart disease or at high risk, medications might be necessary to help lower cholesterol levels or blood pressure.
Conclusion
Understanding what causes a heart attack is the first step towards preventing one. Managing your lifestyle choices and health conditions is crucial in reducing your risk. Regular check-ups and talking to your doctor about your risks and prevention can help you make informed decisions about your heart health.
By recognizing the triggers and mechanisms behind a heart attack, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining heart health and potentially saving lives. Always consult with healthcare professionals for guidance tailored to your personal health needs.