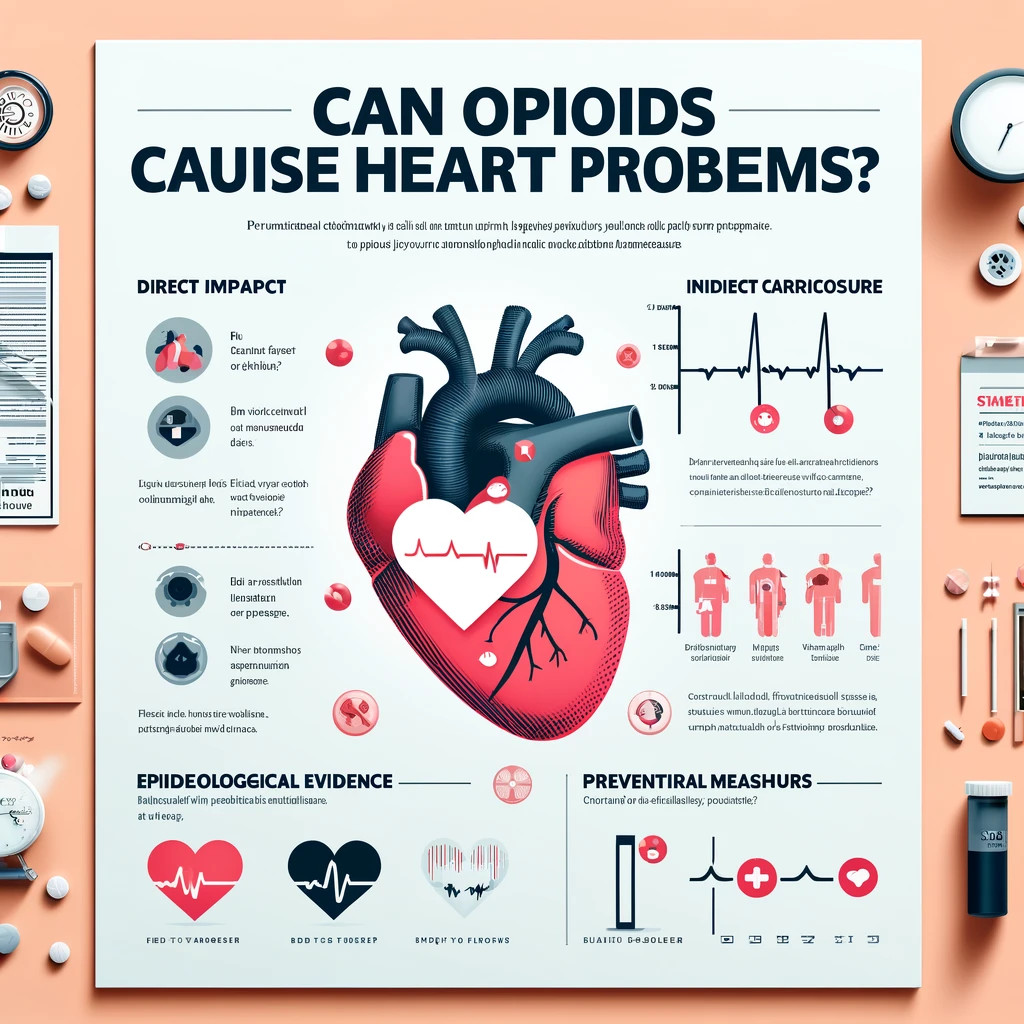
Can Opioids Cause Heart Problems?
Introduction
Opioids, widely used for pain management, have several well-documented side effects, but their impact on heart health is less commonly discussed. This article explores the potential cardiovascular risks associated with opioid use, including heart rhythm disorders, increased risk of heart attacks, and other serious heart-related issues.
Understanding Opioids
Definition and Types
- Natural Opioids: Derived from the opium poppy (e.g., morphine and codeine).
- Semi-synthetic Opioids: Modified forms of natural opioids (e.g., heroin, oxycodone).
- Synthetic Opioids: Chemically manufactured to mimic natural opioids (e.g., fentanyl, methadone).
Mechanism of Action
- Opioids work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas of the body, reducing the perception of pain and promoting feelings of pleasure.
Opioids and Cardiovascular Risk
Direct Impact on Heart Health
- Myocardial Depression: Opioids can depress heart function, reducing the heart’s ability to pump effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Some opioids can disrupt the electrical system of the heart, leading to irregular heart rhythms.
Indirect Cardiovascular Effects
- Hypotension: Opioids can lead to significant drops in blood pressure, which can strain the cardiovascular system.
- Reduced Oxygen Supply: Respiratory depression caused by opioids can decrease oxygen levels, adversely affecting heart health.
Epidemiological Evidence
Research Studies and Findings
- Overview of studies linking opioid use with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events.
- Case studies illustrating specific instances where opioid use has led to heart problems.
Mechanisms Behind Opioids’ Impact on the Heart
Biochemical Pathways
- How opioids interact with cardiac cells and the potential biochemical disruptions that might lead to cardiovascular problems.
Opioid-Induced Systemic Effects
- How systemic effects of opioids, like changes in hormonal balance and inflammation, could contribute to cardiovascular disease.
Risk Factors and Population at Risk
Chronic Users vs. Acute Use
- Differences in cardiovascular risks between chronic opioid users and those using opioids acutely.
Underlying Health Conditions
- How pre-existing health conditions like diabetes or heart disease can exacerbate the cardiovascular risks of opioids.
Preventive Measures and Management
Monitoring and Medical Oversight
- Importance of regular cardiovascular monitoring for patients prescribed opioids, especially those with pre-existing conditions.
Alternatives to Opioid Use
- Non-opioid pain management strategies and their benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion
The potential for opioids to cause heart problems underscores the need for careful management and awareness among healthcare providers and patients alike. By understanding the risks and taking proactive measures, it is possible to mitigate the cardiovascular side effects of these powerful medications.